Death rate curve of microbial population of thermal sterilization.
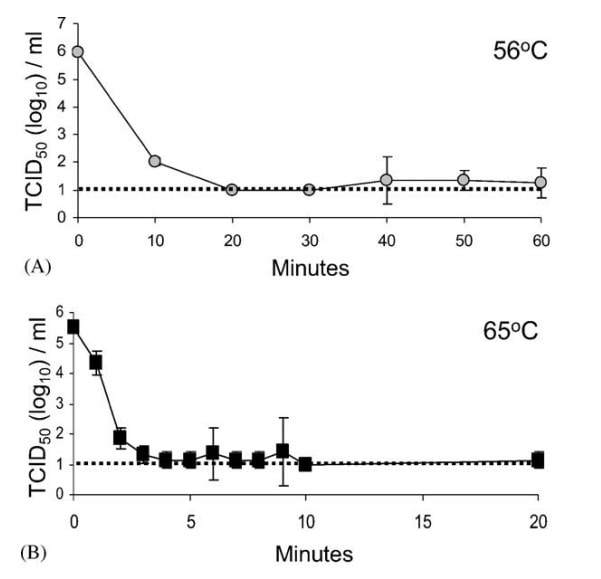
According to scientific publications, bacteria or viruses can be deactivated by heating .
For temperatures above 65 °C (149 °F) is expected to cause near complete inactivation with exposures greater than 3 minutes.
For temperatures between 55 °C and 60 °C (131‐140 °F) heating should last 5 minutes or more.
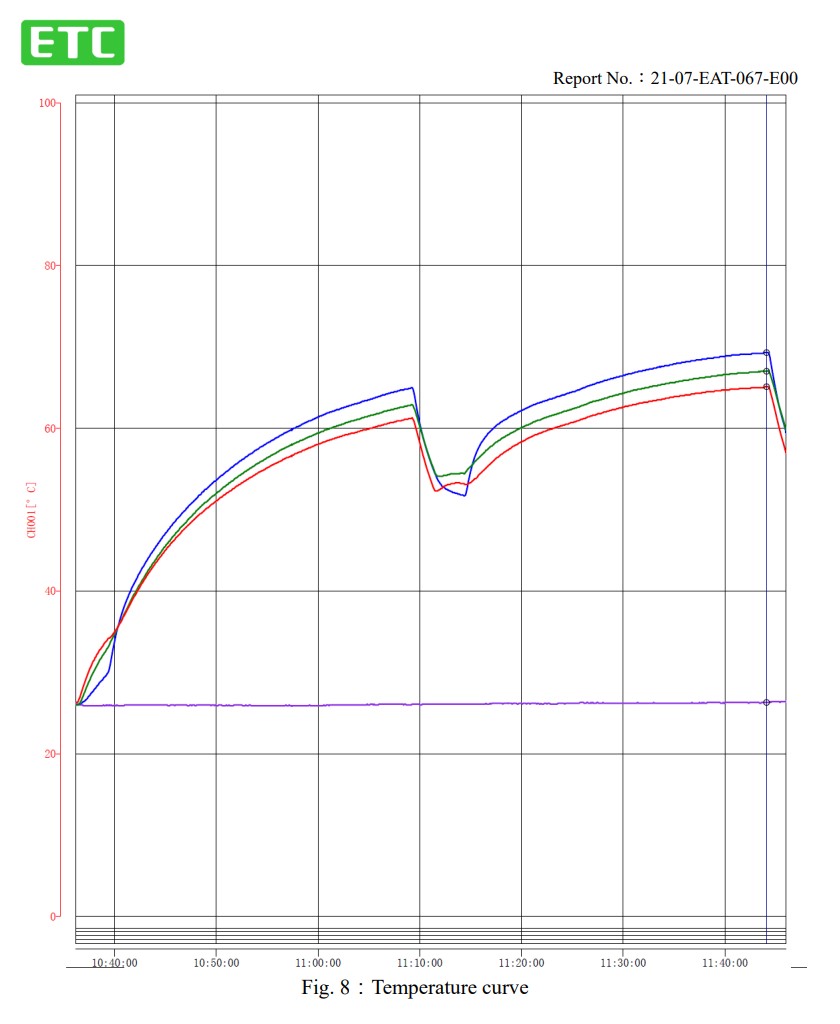
The picture shows two consecutive heating curves inside the sterilization wallet.
According to medical reports and WHO guidance documents, when heating objects containing COVID-19 virus and bacterial microorganisms, the temperature control recommendations are as follows:
- It requires 3 minutes at 75 °C (160 °F).
- It requires 5 minutes at 65 °C (149 °F).
- It requires 30 minutes at 55 °C (131 °F).
This product uses graphene thermal conductive material (functional coating on woven fabric), and is heated and sterilized in a closed space between 55 and 75 degrees C according to the experimental standard.
It can have high thermal conductivity and sterilization efficiency.
It is also very safe for consumers to use.
How C Band Ultraviolet Light Kill The Viruses
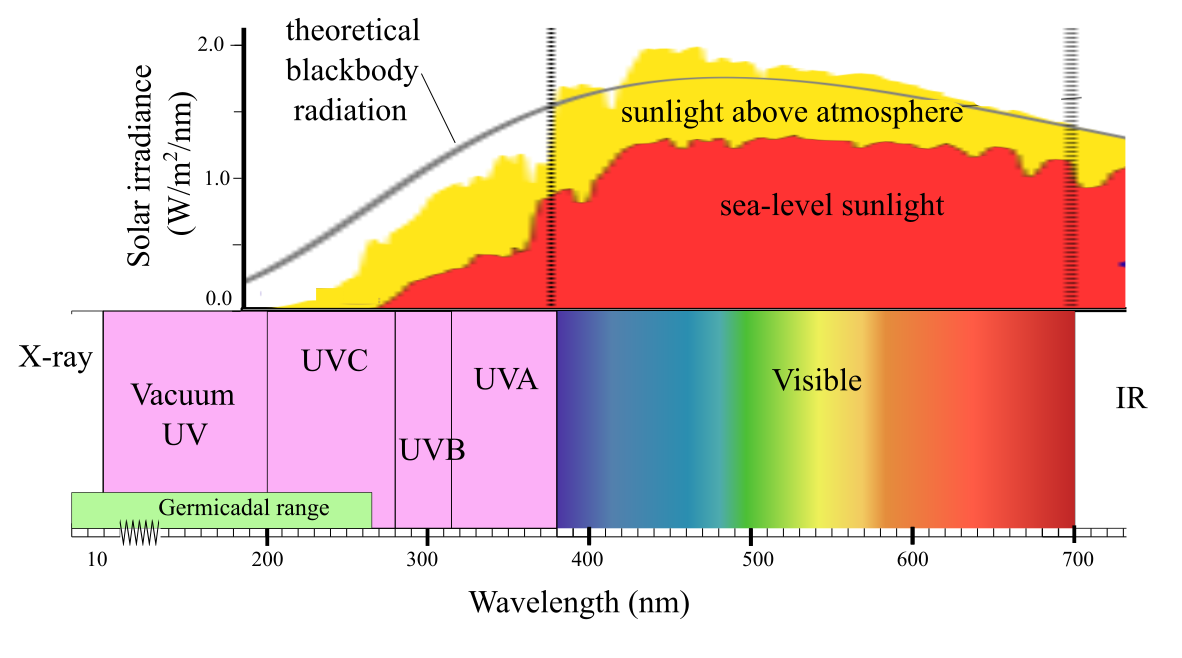
Full Spectrum
The wavelength below 380 nm to 200 nm is ultraviolet light, and the UV ultraviolet light contains three bands UVA, UVB, and UVC. There are three wavelength bands, in which the C band is abbreviated as UVC (see germicidal rang of wavelength).
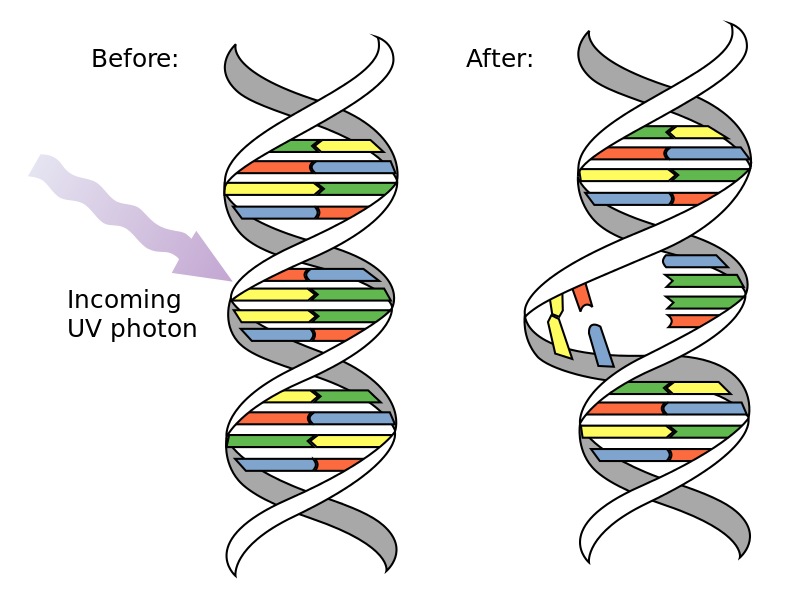
UVC ultraviolet light sterilization principle
Irradiating with UV-C changes the helix structure of DNA and RNA of held by bacteria and viruses, which can inactivate these bacteria and viruses resulting in reducing their proliferation.
UVC Light Can Not Reach The Earth
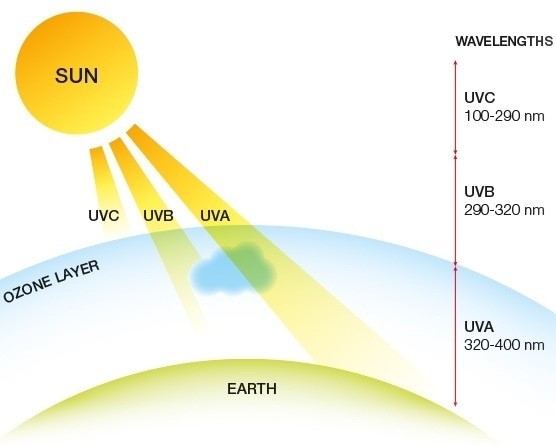
UVC Band of The Sun's Ultraviolet Light
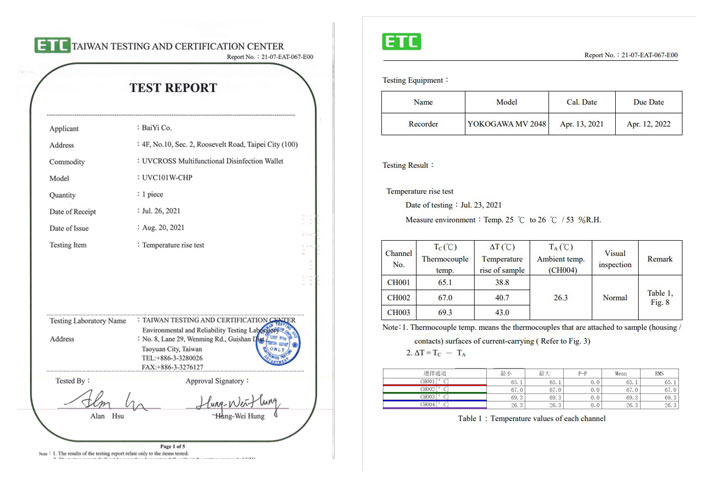
ETC, Taiwan Testing and Certification Center (Temperature Rising Test)
EPA, CE, FCC, IEC62471, EMC

Items where the virus lasts the longest are banknotes and masks!

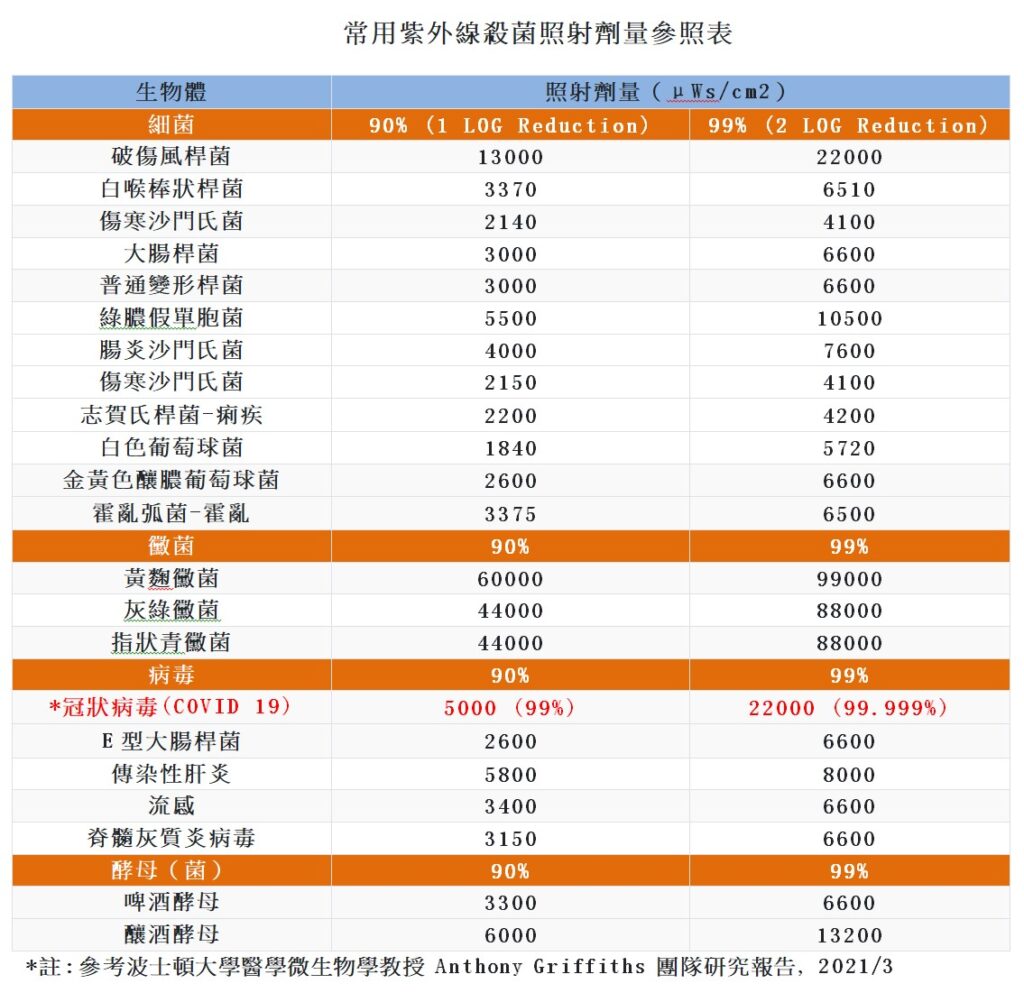
UV Light Dose for Reduction Level